Many walking problems happen when the gear is not right for your dog. You can have better control and comfort if you pick a dog harness and leash that fits your dog’s size, breed, and how active they are. For example, Luna is a Yorkshire Terrier. She had tracheal compression from a retractable leash. This shows the dangers for small dogs.
“Retractable leashes make owners think their dog is safe. For small dogs, these leashes can hurt their trachea. They also make it harder for owners to control their dogs in busy places or traffic.” – Dr. Lisa Chen, DVM
Feature | Harness Leash Set | Retractable Leash |
|---|---|---|
Control Level | High-steady tension, close to you | Low-loose and changes |
Neck Pressure | Minimal-spreads out pressure | High-quick pulls |
Emergency Response | Fast-you can react quickly | Slow-dog may be far away |
Key Takeaways
Pick a harness and leash that match your dog’s size. Make sure it fits how active your dog is. This gives you better control and keeps your dog comfortable.
A harness that fits well lowers the chance of injury. It makes walks better for your dog. Always check if the harness fits before each walk.
Use front-clip harnesses if your dog pulls. These harnesses help stop pulling. They also help your dog stand better during walks.
Check your dog’s gear often for damage or discomfort. Change the straps if you need to keep your dog safe.
Think about how your dog acts and where you walk. This helps you pick the right gear. It can stop problems like slipping or pulling.
What Dog Harness and Leash Can and Cannot Do
Gear Supports Training, Not a Cure-All
You want your walks to be safe and enjoyable. The right gear helps you guide your dog and build good habits. A dog harness and leash can support training, but it does not fix every behavior. You must use patience and practice. If your dog pulls, lunges, or gets distracted, gear can help you manage these moments. Training and consistency matter most.
Safety tip: Gear supports training but cannot guarantee outcomes. Stop use if your dog shows pain, limping, skin injury, distress, or tries to escape repeatedly. Consult a veterinarian for pain or skin issues. Seek a qualified trainer for fear, reactivity, or handling safety.
Fit and Handling Over Features
You may see harnesses with many features. Fit and handling matter more than extra options. A harness that fits well protects your dog’s body and makes walks easier. You should check that the harness sits snug but does not compress fur. The leash attachment point must stay centered. If the harness rotates or rubs, adjust the straps or try a different style.
A well-fitted harness is safer and more effective for daily walks.
Harnesses focus on stress points to prevent discomfort or injury.
Front-clip harnesses help redirect pulling and encourage better posture.
You should always check fit before each walk. Good handling and regular checks keep your dog comfortable.
When to Seek Help for Fear or Reactivity
Some dogs feel nervous or react strongly to other dogs, people, or loud sounds. Gear alone cannot solve fear or reactivity. You should watch for signs like barking, growling, or trying to run away. If you notice these behaviors, ask a qualified trainer for help. Trainers can teach you safe ways to guide your dog and build confidence. For pain or skin problems, contact your veterinarian.
Harness Types and Fit
Choosing the right harness helps you guide your dog safely and comfortably. You need to think about how each style fits and how it affects your dog’s movement. A good fit prevents rubbing and keeps your dog happy during walks.
Overhead vs Step-In Styles
You will see two main ways to put on a harness. Overhead harnesses go over your dog’s head and then buckle around the body. These work well for dogs that stay calm during gear changes. Step-in harnesses let your dog step into the straps before you fasten them. These are easier for dogs that dislike things going over their head. Always check that the harness sits snug to the fur without squeezing.
Y Front vs Straight Chest Strap
Y front harnesses have straps that form a Y shape on your dog’s chest. This design helps redirect pulling and keeps pressure off the throat. Straight chest strap harnesses run across the chest. Some studies show that straight straps can restrict movement, especially when turning or trotting. Y front harnesses often allow better stride and comfort. Vest-style harnesses spread pressure over a wider area, which helps dogs with breathing issues.
Tip: Always check that the chest area stays centered during a short walk. If the harness slides to one side, adjust the straps or try a different style.
Front, Back, Dual Clip Options
Front-clip harnesses attach the leash at the chest. These help you control pulling and guide your dog toward you. Back-clip harnesses attach at the shoulders. These feel comfortable for steady walkers but may give strong dogs more pulling power. Dual-clip harnesses offer both options. You can switch between control and comfort as needed. Make sure the leash attachment point does not drift off center quickly.
Harness Comparison Table
Harness Option | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
Front-Clip No-Pull | Excellent pull control, minimal neck pressure | May twist if fit is poor | Dogs that pull or get excited easily |
Step-In Harness | Easy to put on, low neck pressure | Needs dog to stand still, moderate breathability | Calm walkers needing gentle guidance |
Vest-Style Harness | Very low neck pressure, high comfort | Less control for strong pullers | All-day wear, moderate activity |
Back-Clip Harness | Comfortable, simple to use | Less control, can increase pulling | Calm walkers, seniors, service roles |
You should always measure your dog’s chest behind the front legs and neck where a collar sits. Use a tape snug to the fur, not compressing it. A well-fitted dog harness and leash set supports safe walks and training.
Leash Types and Safety
Choosing the right leash helps you keep your dog safe and comfortable during walks. You need to think about your dog’s behavior, your walking environment, and your activity level. Each leash type offers different levels of control and safety.
Standard Leash for Walks
A standard leash gives you steady control for most walks. You can guide your dog easily in parks or neighborhoods. The smooth grip and simple design make it a good choice for daily use. You should match the leash width to your dog’s size and strength. For small dogs, look for webbing around 0.6-0.8 in (1.5-2.0 cm). Medium dogs often use 0.8-1.0 in (2.0-2.5 cm). Large dogs need 1.0-1.5 in (2.5-3.8 cm).
Long Line for Recall
A long line lets your dog explore while you keep control. You can use it for recall training or practice in open spaces. This leash works best when you have room to move and can watch your dog closely. You need to handle the extra length to avoid tangles. Long lines help build trust and give your dog controlled freedom.
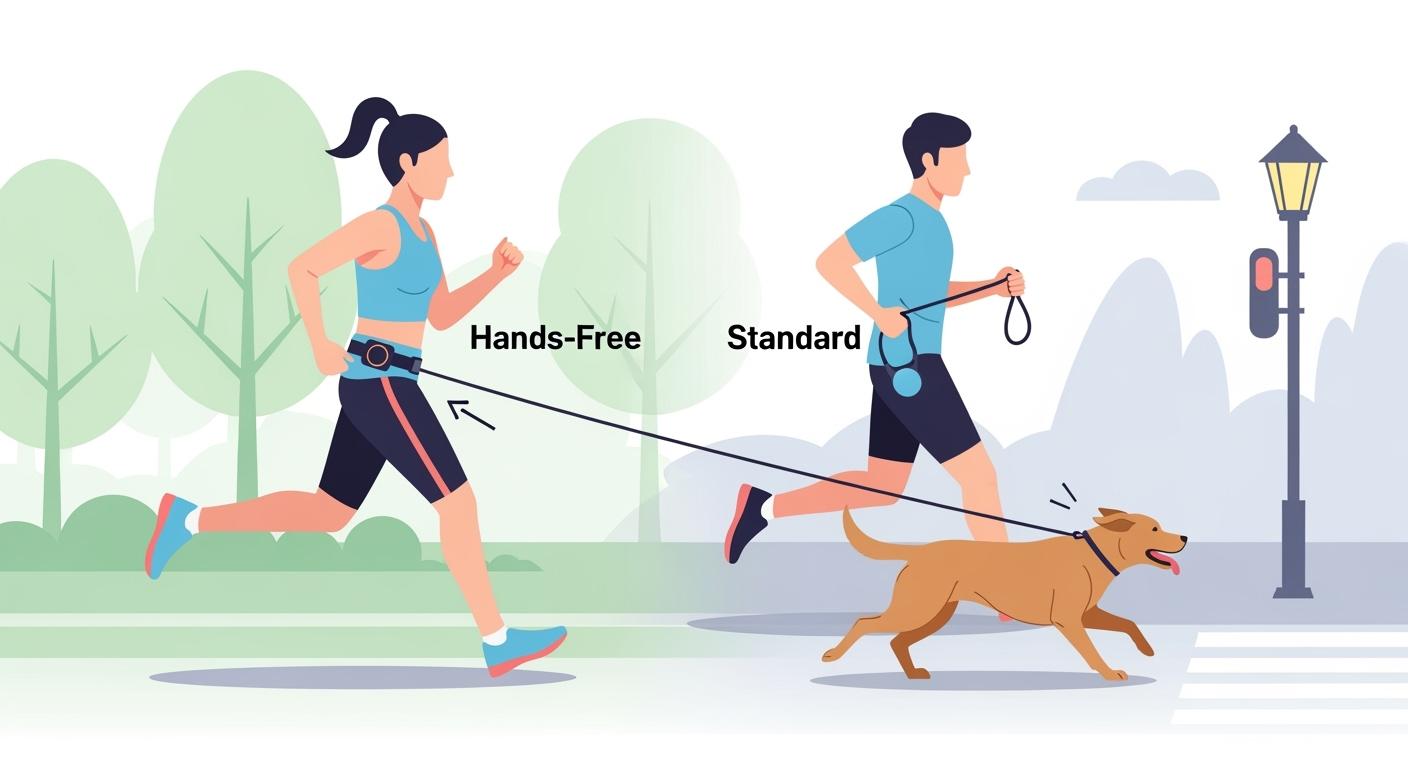
Hands-Free for Running
Hands-free leashes attach to your waist or belt. You can run or hike without holding the leash. This style reduces hand fatigue and supports natural movement. You should use a hands-free leash only if your dog responds well to commands. Good training is important for safety.
Retractable Leash Risks
Retractable leashes can create sudden tension and tangles, especially in busy areas. You may find it harder to control your dog quickly. Some experts warn about injuries from these leashes.
“Unfortunately, retractable leashes often make controlling dogs in stressful situations more challenging. They can also result in injuries to both our four-legged friends as well as their human companions. I, unfortunately, have treated many dog patients with lacerations requiring stitches from being entangled in retractable leashes.”
You should use extra caution if you choose a retractable leash. Always check your surroundings and keep your dog close in crowded places.
Leash Comparison Table
Leash Option | Pros | Cons | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
Standard Leash | Good control for most walks | May not suit crowded areas | Parks or neighborhoods |
Long Line | Great for recall training, controlled freedom | Can be cumbersome, risk of tangles | Training, open spaces |
Hands-Free Leash | Allows natural movement, reduces hand fatigue | Needs well-trained dog | Running, hiking |
Retractable Leash | Adjustable length, more freedom | Sudden tension, injury risk, less control | Open areas with few distractions |
You can match your dog harness and leash to your routine for safer, happier walks.
Measuring and Sizing for Dog Harness and Leash

Choosing the right size for your dog’s gear is the foundation for safe and comfortable walks. You need to measure your dog carefully and select the correct strap and hardware width. This step helps you avoid common problems like slipping, rubbing, or escape risk.
Chest and Neck Measurement Points
You should measure your dog’s chest and neck before buying a harness. Use a soft measuring tape. Place the tape around the widest part of the chest, just behind the front legs. For the neck, measure where a collar would sit. Keep the tape snug against the fur, but do not compress it. These measurements help you pick a harness that distributes pressure evenly and prevents discomfort.
A harness that fits well supports your dog’s shoulders and chest.
Proper fitting helps prevent shifting, rubbing, or escape.
Good measurements make training more effective and keep your dog safe.
Tip: Always double-check your measurements before ordering. A harness that fits well lasts longer and keeps your dog comfortable.
Strap and Hardware Width by Dog Size
Strap width and hardware size matter for both comfort and durability. You need to match the strap width to your dog’s size and strength. Wider straps can spread pressure better, but they should not block shoulder movement.
Small dogs often use webbing that is 0.6-0.8 in (1.5-2.0 cm) wide.
Medium dogs usually need 0.8-1.0 in (2.0-2.5 cm) wide straps.
Large dogs benefit from 1.0-1.5 in (2.5-3.8 cm) wide straps.
Choose hardware that feels sturdy and smooth. Make sure the buckles and clips are easy to use and do not pinch your dog’s skin.
Leash Length and Width Choices
Leash length and width affect control and safety. You should select a leash that matches your dog’s size and your walking environment. Shorter leashes work best in busy areas. Longer leashes give more freedom in open spaces.
Dog Size/Weight Category | Recommended Leash Width | Recommended Leash Length |
|---|---|---|
Show Dogs | 1/8 in (0.3 cm) | 1-8 ft (0.3-2.4 m) |
Dogs under 50 lbs | 3/8 in (1.0 cm) | 3-6 ft (0.9-1.8 m) |
Dogs over 50 lbs | 1/2 in (1.3 cm) | 3-6 ft (0.9-1.8 m) |
Leash Length | Best For |
|---|---|
4 feet (1.2 m) | Urban settings, high traffic, distractions |
6 feet (1.8 m) | Parks, neighborhoods, relaxed walks |
8-10 feet (2.4-3.0 m) | Open spaces, training, more freedom |
You should match leash width to your dog’s strength and the hardware size. Smooth edges and a comfortable grip help prevent hand fatigue.
Measurement Table
Use this table to guide your measuring and fit checks. Accurate measurements help you select the best dog harness and leash for your routine.
What to Measure | How to Measure | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Chest Girth | Wrap tape around widest part, just behind front legs | Ensures harness fits and distributes pressure safely |
Neck Girth | Measure where collar sits, snug to fur, no compression | Prevents choking, keeps harness stable |
Strap Width | Check product specs for width by dog size | Comfort and durability, avoids rubbing |
Leash Length | Choose based on walk environment and dog size | Matches control needs and activity level |
Two Finger Check | Slide two fingers under harness at chest, neck, belly | Prevents pinching, allows movement |
Movement Test | Observe dog walking, check for shifting or rubbing | Flags poor fit, helps avoid escape risk |
Backward Pressure | Apply gentle backward pull on leash | Checks for slipping, signals need for adjustment |
Note: Always re-check fit after grooming or coat changes. Adjust straps if you notice shifting or rubbing during walks.
A well-measured and fitted dog harness and leash set helps you solve common walking problems. You can keep your dog safe, comfortable, and ready for every adventure.
Fit Checks and Setup Routine
Adjustment Order for Even Fit
You want your dog harness and leash to fit well every time. Start by placing the harness on your dog. Adjust the largest straps first, usually around the chest. Move to the side straps, then the belly strap. Check for symmetry so the harness sits evenly. Make sure the harness sits below the throat and behind the front legs. Secure all clips and attachment points.
Setup Checklist Table
Check | Pass Sign | What to Adjust |
|---|---|---|
Chest strap snug, not tight | Two fingers fit | Loosen or tighten chest strap |
Harness centered | Stays in middle | Adjust side straps |
Leash clip secure | No movement | Recheck attachment |
No rubbing or redness | Skin clear | Adjust strap or try new style |
Dog moves freely | Walks, sits, turns | Loosen or reposition straps |
Two Finger, Centering, Rotation Rules
Use the two-finger rule at the chest, neck, and belly. You should fit two fingers between the harness and your dog’s body without pressing into the skin. The chest area must stay centered during a short walk. If the leash attachment point drifts off center, adjust the straps or try a different harness style. These checks help prevent rubbing and slipping.
Tip: Always check for strap drift or rotation after your dog moves. A harness that rotates or shifts may need a different adjustment.
Movement Test and Hotspot Scan
Ask your dog to walk, sit, lie down, and turn. Watch for any signs of discomfort or slipping. After a walk, inspect the jawline, throat, armpit, shoulder, and buckle contact points for redness or irritation. These steps help you catch problems early.
Movement Test and Hotspot Scan Table
Test/Scan Type | Description |
|---|---|
Two-Finger Rule | Check the fit by ensuring you can fit two fingers between the harness and your dog’s body. |
Hotspot Scan | Inspect areas along the jawline, throat, and strap edges for redness or irritation. |
Walk Test | Observe your dog’s behavior while walking to check for discomfort or harness slipping. |
Parameter and Value Table
Use this table to guide your fit checks and adjustments. Each parameter helps you keep your dog safe and comfortable.
Parameter | Target range or option | Why it matters |
|---|---|---|
Chest measurement | widest chest, behind front legs | Primary sizing baseline |
Neck measurement | where collar sits | Comfort and stability cue |
Tape snug rule | snug, no fur compression | Prevents false small readings |
Harness type | overhead or step-in | Changes put-on steps and fit feel |
Clip option | front, back, dual | Changes control and rotation risk |
Leash type | standard, long line, hands-free | Changes handling and safety needs |
Fit check | two finger rule | Reduces pinch and rub risk |
Centering rule | chest stays centered | Flags poor adjustment |
Rotation cue | leash point drifts off center | Flags layout or fit issue |
Hotspot scan | throat, armpit, shoulder, buckles | Catches rubbing early |
Slip test cue | gentle backward pressure check | Signals fit or style change needed |
Width cues | 0.6-1.5 in (1.5-3.8 cm) | Comfort feel and durability cue |
Re-check routine | after a few wears and coat changes | Prevents gradual misfit |
Fit Check Steps for Safety and Comfort
Measure your dog’s chest and neck girth.
Choose a harness style that fits your dog’s body and activity level.
Use the size chart to select the appropriate size.
Place the harness on your dog and adjust the largest straps first.
Work down to the smaller straps for a balanced fit.
Ensure the harness sits below the throat and behind the front legs.
Check that the leash clips and attachment points are secure.
Test the fit while your dog moves by asking them to walk, sit, lie down, and turn.
Look for any strap drift or rubbing.
Perform a hotspot scan after a walk to check for signs of discomfort.
You can keep your dog harness and leash working well by following these steps and checking fit often.
Decision Guide: Match Dog and Routine to Gear
Choosing the right gear for your dog starts with understanding their behavior and your walking environment. You want to solve problems like pulling, slipping, or skin irritation. This guide helps you match harness and leash features to your dog’s needs and your routine.
Strong Pullers and Busy Areas
If your dog pulls hard or you walk in busy places, you need gear that gives you control and keeps your dog safe. Heavy-duty webbing leashes work well for large, strong breeds. These leashes resist fraying and have high tensile strength. Double-handled training leashes offer multiple grip points, so you can guide your dog in crowded areas. Bungee leashes absorb shock when your dog lunges, which protects both you and your dog from sudden jolts.
Tip: Use a front-clip harness to help redirect pulling. Check that the harness stays centered and does not twist. Adjust straps for a snug fit without compressing fur.
Leash Type Comparison Table
Leash Type | Best For | Pros | Cons | Recommended Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Heavy-Duty Webbing Leash | Large, powerful breeds | Durable, resists fraying, high strength | Bulkier, heavier | Daily walks, urban environments |
Double-Handled Training Leash | Dogs in training, reactive behaviors | Multiple grip points, better control | More complex to use | Distraction-heavy areas |
Bungee Leash | Dogs that lunge suddenly | Shock-absorbing, reduces jolt | Less precise control | Hiking, trail walks |
Nervous Dogs and Slip Risk
Nervous dogs may try to back out of their harness or resist gear. You can reduce slip risk by choosing a harness that fits well and introduces low pressure. Start with a calm introduction. Let your dog sniff and explore the harness before putting it on. Adjust the chest area first, then side straps, then belly strap. Check for symmetry and make sure the harness sits below the throat and behind the front legs.
Choose a harness with a snug fit, not tight.
Use the two-finger rule at all contact points.
Test with gentle backward pressure to check for slipping.
Re-check fit after grooming or coat changes.
Note: A step-in harness can help dogs that dislike overhead motion. Always check for strap drift and rotation during walks.
Sensitive Skin and Rubbing
Dogs with sensitive skin need harnesses made from soft, breathable materials. Neoprene offers soft cushioning and resists mold and bacteria. Polyester mesh promotes airflow and keeps your dog cool, but may stretch over time. Fleece or flannel linings feel cozy but can trap heat. Ripstop with fleece gives a cushioned feel but may retain moisture.
Harness Material Table
Material | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
Neoprene | Soft, hypoallergenic, resists mold | None mentioned, ideal for active dogs |
Polyester Mesh | Lightweight, breathable | Stretches over time, not for strong pullers |
Nylon and Polyester | Strong, easy to clean | Can chafe without padding |
Biothane, Leather | Waterproof, molds to shape | Heavier, less breathable |
Fleece or Flannel | Cozy, soft lining | Traps heat, risk of overheating |
Ripstop with Fleece | Cushioned, widely available | Retains heat and moisture |
Tip: Always scan for hotspots after walks. Check the throat, armpit, shoulder, and buckle contact points for redness or irritation.
Decision Table
Use this table to match your dog’s profile and walk context to the best gear choices. Avoid gear that increases risk or discomfort.
Dog Profile/Context | Best Harness Features | Best Leash Choice | What to Avoid |
|---|---|---|---|
Strong puller, busy area | Front-clip, Y-front, wide straps | Double-handled, heavy-duty webbing | Thin straps, back-clip only |
Nervous, slip risk | Step-in, snug fit, escape-proof | Standard leash, short length | Loose fit, overhead only |
Sensitive skin, prone to rubbing | Neoprene, mesh, padded edges | Smooth grip, lightweight | Rough webbing, unpadded straps |
Calm walker, open space | Back-clip, vest-style, soft lining | Long line, hands-free | Retractable leash in busy areas |
Scenario A: Dog Pulls and Harness Twists
You notice your dog pulls and the harness twists during walks. Choose a front-clip, Y-front harness with wide straps. Use a double-handled leash for better control. Adjust the chest area first, then side straps, then belly strap. Check that the harness stays centered. Use the two-finger rule and test for rotation. If the leash attachment point drifts off center, re-adjust or try a different style.
Scenario B: Dog Resists Gear or Backs Out When Startled
Your dog resists gear or tries to back out when startled. Start with a low-pressure introduction. Let your dog sniff the harness. Use a step-in style for easier handling. Adjust straps for a snug fit. Test with gentle backward pressure to check for slip risk. Use a standard leash with a short length for better control. Re-check fit after grooming or coat changes.
Step-by-Step Decision Process
Choose harness and leash type using the decision table.
Measure your dog’s chest and neck. Select size. Adjust in order: chest area, side straps, belly strap, symmetry check.
Pick clip strategy. Match leash style to your walking environment.
Run fit tests: two-finger check, movement test, gentle backward pressure test for slip risk.
Do a short practice walk. Re-check hotspots, rotation, and handling comfort.
You can solve common walking problems by matching your dog harness and leash to your dog’s profile and routine. This approach helps you keep your dog safe, comfortable, and ready for every walk.
Retail Notes and OEM/ODM Explained
Listing Copy for Fit and Handling
When you read a product listing, you want clear details that help you choose the right harness and leash. Look for these features in the copy:
Heavy-duty materials and reinforced hardware provide secure control.
Padded handles offer a comfortable grip for long walks.
Breathable, padded materials reduce strain and prevent rubbing.
Reinforced stitching and reflective trim increase durability and visibility.
Reflective safety trim boosts visibility during low-light walks.
Quick-snap buckles make it easy to put on and take off the harness.
Four-way adjustability ensures a secure fit for dogs of all sizes.
Built-in ID pocket lets you store your dog’s tag for security.
These points help you compare products and find gear that matches your dog’s needs.
Size Chart and Spec Checklist
A clear size chart and specification checklist help you pick the right size and reduce returns. You should measure your dog’s girth, neck, and back length before ordering.
Measurement | Description | Suggested Size |
|---|---|---|
Girth | Widest part of rib cage | Medium: 20-30 inches (51-76 cm) |
Neck | Base of neck to brisket | Small: 10-14 inches (25-36 cm) |
Back Length | Base of neck to tail base | Small: under 12 inches (30 cm) |
Always check the product’s size chart and measure your dog with a snug tape, not compressing the fur.
Return Reduction and Care Routine
You can lower the chance of returns by following a simple care routine. Measure your dog before buying. Check fit after grooming or coat changes. Adjust straps for comfort and safety. Clean harnesses and leashes regularly with mild soap and water. Inspect for wear and replace gear if you see fraying or broken hardware.
Tip: Re-check fit after a few wears. This helps prevent gradual misfit and keeps your dog safe.
OEM and ODM Explainer
You may see the terms OEM and ODM when shopping for harnesses and leashes. OEM stands for Original Equipment Manufacturer. This means a brand creates products based on its own designs or specifications, giving full control over materials and structure. ODM stands for Original Design Manufacturer. This lets buyers choose from existing designs that can be customized, making it easier for new brands or wholesalers to expand quickly. OEM works well for brands with clear product ideas. ODM suits buyers who want faster market entry and less design work.
You can choose the right dog harness and leash by following a few clear steps:
Assess your dog’s needs and walking routine.
Compare harness and leash types for your situation.
Measure your dog for a proper fit.
Check fit and comfort before each walk.
Match your gear to your daily routine.
Remember, comfort, safety, and adjustability matter most. Good gear supports training, but patience and practice help you succeed. Use this guide to make informed choices for safer, happier walks.
FAQ
How do you measure your dog for a harness?
Use a soft tape. Measure the chest behind the front legs. Measure the neck where a collar sits. Keep the tape snug to the fur, not tight. Double-check your numbers before you buy.
What harness style works best for strong pullers?
Front-clip and Y-front harnesses help you redirect pulling. Wide straps spread pressure. Always check that the harness stays centered and does not twist during walks.
How often should you check harness fit?
Check fit before each walk. Re-check after grooming or coat changes. Look for strap drift, rubbing, or signs of discomfort. Adjust straps as needed to keep your dog safe.
Can you use a harness and leash for training?
Yes, you can use a harness and leash to support training. Choose gear that fits well and matches your dog’s activity level. Practice handling and reward calm walking.
What should you do if your dog tries to slip out of the harness?
Test with gentle backward pressure. If your dog slips out, adjust the straps for a snug fit. Try a step-in or escape-proof harness. Always use the two-finger rule at contact points.